Apache curator ZooKeeper 分布式锁源码阅读
工作中 redis 分布式锁和 zk 分布式锁都用,这篇文章想深入了解一下 zk 分布式锁的使用以及底层源码,目前业界主流的客户端是 curator,本文也准备以 curator 做为客户端。我选用的是最新的4.3.0版本,可能不同版本有些许不同。
Curator 的官网提供了示例:https://curator.apache.org/getting-started.html
InterProcessMutex lock = new InterProcessMutex(client, lockPath);
if (lock.acquire(maxWait, waitUnit)) {
try {
// do some work inside of the critical section here
} finally {
lock.release();
}
}
1 先看看官方示例
1.1 加锁
加锁重点关注加锁成功的流程、加锁失败的流程、重复加锁的流程。
先来看看第一次加锁的流程 Curator 是如何封装的:
private boolean internalLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception
{
/*
Note on concurrency: a given lockData instance
can be only acted on by a single thread so locking isn't necessary
*/
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
LockData lockData = threadData.get(currentThread);
if ( lockData != null )
{
// re-entering
lockData.lockCount.incrementAndGet();
return true;
}
String lockPath = internals.attemptLock(time, unit, getLockNodeBytes());
if ( lockPath != null )
{
LockData newLockData = new LockData(currentThread, lockPath);
threadData.put(currentThread, newLockData);
return true;
}
return false;
}
可以清晰地知道先做了可重入锁的支持,利用 ConcurrentHashMap 保存了每次获取锁的信息(线程和lockPath)。
再往下 debug:
@Override
public String createsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, String path, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception
{
String ourPath;
if ( lockNodeBytes != null )
{
ourPath = client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath(path, lockNodeBytes);
}
else
{
ourPath = client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath(path);
}
return ourPath;
}
可以看到创建路径的时候,其实是创建了一个临时顺序节点。在创建完路径之后,就是判断是否能获取锁的逻辑了。
ourPath = driver.createsTheLock(client, path, localLockNodeBytes);
hasTheLock = internalLockLoop(startMillis, millisToWait, ourPath);
debug 进入 internalLockLoop:只截取了部分关键代码
while ( (client.getState() == CuratorFrameworkState.STARTED) && !haveTheLock )
{
List<String> children = getSortedChildren();
String sequenceNodeName = ourPath.substring(basePath.length() + 1); // +1 to include the slash
PredicateResults predicateResults = driver.getsTheLock(client, children, sequenceNodeName, maxLeases);
if ( predicateResults.getsTheLock() )
{
haveTheLock = true;
}
else {
...
}
}
又调用了 getsTheLock 方法:
public PredicateResults getsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception
{
int ourIndex = children.indexOf(sequenceNodeName);
validateOurIndex(sequenceNodeName, ourIndex);
boolean getsTheLock = ourIndex < maxLeases;
String pathToWatch = getsTheLock ? null : children.get(ourIndex - maxLeases);
return new PredicateResults(pathToWatch, getsTheLock);
}
流程就是先判断当前节点是否是正序第一个节点以及获取当前节点的上一节点,方便监听。
如果是已经加锁了,此时第二个客户端来获取锁,由于创建的是临时顺序节点,因为不是正序第一个节点,那么就会加锁失败,加锁失败之后,还有一些逻辑:
synchronized(this)
{
try
{
// use getData() instead of exists() to avoid leaving unneeded watchers which is a type of resource leak
client.getData().usingWatcher(watcher).forPath(previousSequencePath);
if ( millisToWait != null )
{
millisToWait -= (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis);
startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
if ( millisToWait <= 0 )
{
doDelete = true; // timed out - delete our node
break;
}
wait(millisToWait);
}
else
{
wait();
}
}
catch ( KeeperException.NoNodeException e )
{
// it has been deleted (i.e. lock released). Try to acquire again
}
}
可以看到加锁失败之后,对上一节点加了一个 watcher 监听器,监听它是否还存在,同时 zk 分布式锁是支持时效时间的,否则线程会一直 wait。
1.2 释放锁
释放锁的流程相对比较简单,主要是删除当前节点以及对应的线程加锁信息。
public void release() throws Exception
{
/*
Note on concurrency: a given lockData instance
can be only acted on by a single thread so locking isn't necessary
*/
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
LockData lockData = threadData.get(currentThread);
if ( lockData == null )
{
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException("You do not own the lock: " + basePath);
}
int newLockCount = lockData.lockCount.decrementAndGet();
if ( newLockCount > 0 )
{
return;
}
if ( newLockCount < 0 )
{
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException("Lock count has gone negative for lock: " + basePath);
}
try
{
internals.releaseLock(lockData.lockPath);
}
finally
{
threadData.remove(currentThread);
}
}
额外需要注意的一个流程就是当前线程释放锁之后,其他线程是如何获取锁的?
其实当前线程释放锁的时候会利用 watcher,这样下一个节点对应的线程就可以再次去请求获取锁,由此我们也可以知道默认情况下是公平锁。
2 Semaphore
首先抛一个问题,Curator 是如何实现 Semaphore 的呢?普通的锁只能支持一个线程获取到锁。还是按照官方示例代码,一步步debug 吧。
代码参考:https://curator.apache.org/curator-recipes/shared-semaphore.html
public InterProcessSemaphoreV2(CuratorFramework client,
String path,
int numberOfLeases)
Parameters:
client - client
path - the path to lock
numberOfLeases - the number of leases allowed by this semaphore
InterProcessSemaphoreV2 semaphoreV2 = new InterProcessSemaphoreV2(client, lockPath, 3);
Lease lease = semaphoreV2.acquire();
Thread.sleep(1000);
semaphoreV2.returnLease(lease);
debug 发现在 new InterProcessSemaphoreV2(client, lockPath, 3)底层其实是新创建了一个path 以 "/locks"结尾的锁lock = new InterProcessMutex(client, ZKPaths.makePath(path, LOCK_PARENT));, 另外还创建了一个以 “/leases" 结尾的path。
private InterProcessSemaphoreV2(CuratorFramework client, String path, int maxLeases, SharedCountReader count)
{
this.client = client.newWatcherRemoveCuratorFramework();
path = PathUtils.validatePath(path);
lock = new InterProcessMutex(client, ZKPaths.makePath(path, LOCK_PARENT));
this.maxLeases = (count != null) ? count.getCount() : maxLeases;
leasesPath = ZKPaths.makePath(path, LEASE_PARENT);
if ( count != null )
{
count.addListener
(
new SharedCountListener()
{
@Override
public void countHasChanged(SharedCountReader sharedCount, int newCount) throws Exception
{
InterProcessSemaphoreV2.this.maxLeases = newCount;
client.postSafeNotify(InterProcessSemaphoreV2.this);
}
@Override
public void stateChanged(CuratorFramework client, ConnectionState newState)
{
// no need to handle this here - clients should set their own connection state listener
}
}
);
}
}
在获取锁的时候,我们还可以进一步可看到核心的逻辑如下:
PathAndBytesable<String> createBuilder = client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL);
String path = (nodeData != null) ? createBuilder.forPath(ZKPaths.makePath(leasesPath, LEASE_BASE_NAME), nodeData) : createBuilder.forPath(ZKPaths.makePath(leasesPath, LEASE_BASE_NAME));
String nodeName = ZKPaths.getNodeFromPath(path);
lease = makeLease(path);
每一次获取锁的时候,都会去 lease path 下创建新的节点。
看到这里,Semaphore 的底层实现就比较明了了,可以参考下图:
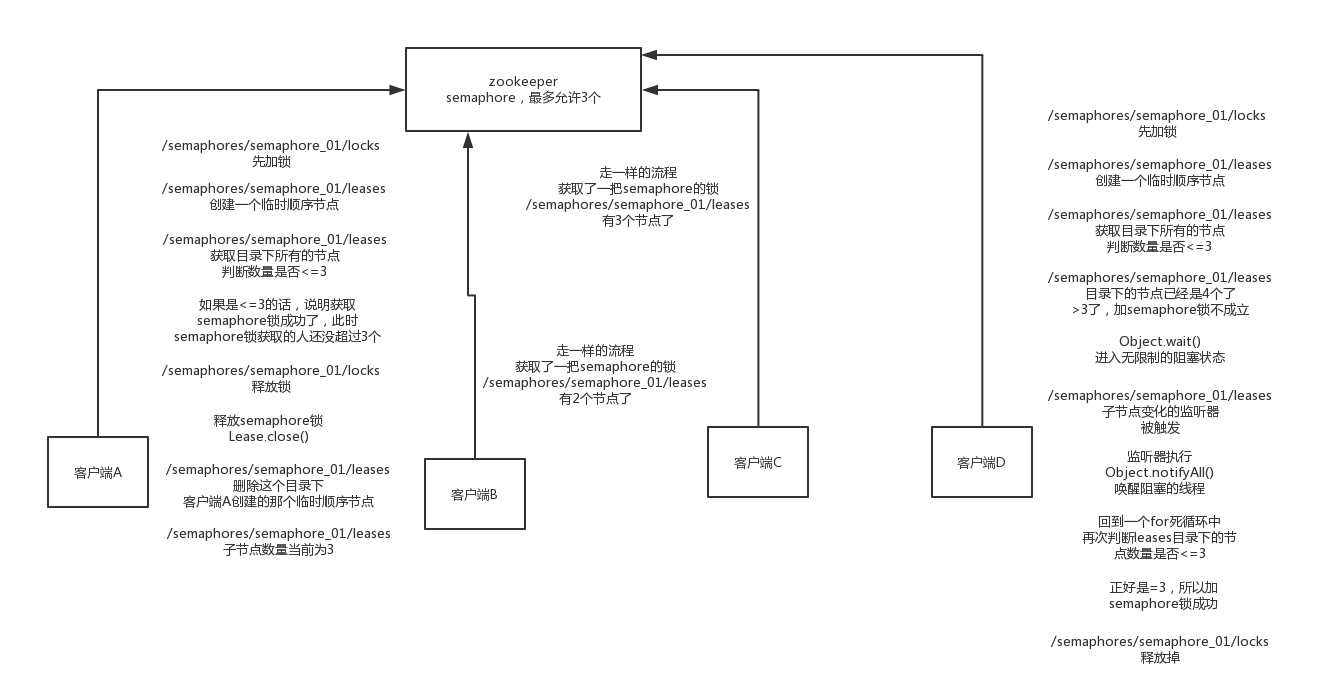
3 非可重入锁
非可重入锁的实现其实是利用了 Semaphore,就是在构造 InterProcessSemaphoreV2时, numberOfLeases 设置为1。
public InterProcessSemaphoreV2(CuratorFramework client,
String path,
int numberOfLeases)
Parameters:
client - client
path - the path to lock
numberOfLeases - the number of leases allowed by this semaphore
4 读锁与写锁
4.1 读锁 + 读锁
读写锁的基本使用示例: https://curator.apache.org/curator-recipes/shared-reentrant-read-write-lock.html
public InterProcessReadWriteLock(CuratorFramework client,
String basePath)
Parameters:
client - the client
basePath - path to use for locking
写一个简单demo, debug 一下:
InterProcessReadWriteLock lock = new InterProcessReadWriteLock(client, lockPath);
lock.readLock().acquire();
Thread.sleep(1000);
lock.readLock().release();
lock.writeLock().acquire();
lock.writeLock().release();
创建读锁的时候,底层会创建一个包含 READ 路径的节点,基本流程与创建普通锁的流程一致。
private final InterProcessMutex readMutex;
...
readMutex = new InternalInterProcessMutex
(
client,
basePath,
READ_LOCK_NAME,
lockData,
Integer.MAX_VALUE,
new SortingLockInternalsDriver()
{
@Override
public PredicateResults getsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception
{
return readLockPredicate(children, sequenceNodeName);
}
}
);
private PredicateResults readLockPredicate(List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName) throws Exception
{
if ( writeMutex.isOwnedByCurrentThread() )
{
return new PredicateResults(null, true);
}
int index = 0;
int firstWriteIndex = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int ourIndex = -1;
for ( String node : children )
{
if ( node.contains(WRITE_LOCK_NAME) )
{
firstWriteIndex = Math.min(index, firstWriteIndex);
}
else if ( node.startsWith(sequenceNodeName) )
{
ourIndex = index;
break;
}
++index;
}
StandardLockInternalsDriver.validateOurIndex(sequenceNodeName, ourIndex);
// firstWriteIndex: Interger max 值
boolean getsTheLock = (ourIndex < firstWriteIndex);
String pathToWatch = getsTheLock ? null : children.get(firstWriteIndex);
return new PredicateResults(pathToWatch, getsTheLock);
}
加读锁的处理逻辑比较简单,只是创建一个节点,判断当前节点的索引位置小于 Integer 最大值即可。
由此我们也可以知道不管是不是同一个线程,获取读锁都是不互斥的。
4.2 读锁 + 写锁
InterProcessReadWriteLock lock = new InterProcessReadWriteLock(client, lockPath);
lock.readLock().acquire();
lock.writeLock().acquire();
debug 一下先加读锁再加写锁:
writeMutex = new InternalInterProcessMutex
(
client,
basePath,
WRITE_LOCK_NAME,
lockData,
1,
new SortingLockInternalsDriver()
{
@Override
public PredicateResults getsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception
{
return super.getsTheLock(client, children, sequenceNodeName, maxLeases);
}
}
);
@Override
public PredicateResults getsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception
{
int ourIndex = children.indexOf(sequenceNodeName);
validateOurIndex(sequenceNodeName, ourIndex);
boolean getsTheLock = ourIndex < maxLeases;
String pathToWatch = getsTheLock ? null : children.get(ourIndex - maxLeases);
return new PredicateResults(pathToWatch, getsTheLock);
}
可以看到如果想要获取到写锁,那么写锁对应节点的index 必须小于 maxLeases,但在debug 时,发现 maxleases = 1,明显是不符合条件的,所以加完读锁再加写锁是不可行的。
4.3 写锁 + 读锁
代码debug 流程基本一致,这里不再赘述,直接说结论:同一线程,写锁+读锁可行,不同线程写锁+读锁不可行。
4.4 写锁 + 写锁
不管是不是同一线程,都不行。